The four major components of the refrigeration system are compressor, evaporator, condenser and throttling device. The role of the condenser in the refrigeration system is mainly to cool and liquefy the gaseous refrigerant in the high temperature and high pressure state discharged from the compressor, so as to meet the requirements of the circulating use of the refrigerant in the system. The selection of the temperature difference between the condensing temperature and the coolant inlet and outlet involves economic issues in the refrigeration system. Increasing the condensation temperature and reducing the temperature difference between the coolant inlet and outlet can increase the heat transfer temperature difference, reduce the required heat transfer area, and reduce the investment cost of heat exchange equipment.
However, lowering the condensing temperature can reduce the power consumption of the refrigeration compressor. The greater the temperature difference between the coolant inlet and outlet, the less the refrigerant flow required, and the less energy consumption (water pumps and fans) for transportation, thereby reducing operating costs. . Therefore, it is necessary to weigh the advantages and reasonably determine the temperature difference between the condensation temperature and the coolant inlet and outlet temperature. There are many types of condensers. The following mainly introduces the working principles and structural characteristics of several common condensers.
1. Features of horizontal shell and tube condenser
The appearance of the condenser
The closed shell and tube condenser in which the cooling water flows horizontally through the tube bundle under pressure is often used in large and medium-sized ammonia or Freon refrigeration devices. The horizontal shell and tube condenser has the following characteristics:
(1) Horizontal installation, multi-channel water flow, high flow rate.
(2) The large temperature difference between inlet and outlet water can reduce the amount of cooling water.
(3) The cooling water temperature is 4-6℃; the heat transfer coefficient is higher than that of the vertical type.
(4) Compact structure and small floor space.
(5) The cooling water temperature rises greatly and the water consumption is small.
2. Features of vertical shell and tube condenser
The open tube condenser in which the cooling water flows down the tube by gravity is often used in medium and large ammonia refrigeration plants. The horizontal shell and tube condenser has the following characteristics:
(1) The cooling water has a large flow rate, a high flow rate, and a high heat transfer coefficient.
(2) The vertical installation area is small and can be installed outdoors.
(3) Cooling water flows straight through and has a large flow rate, which does not require high water quality. Generally, water sources can be used as cooling water.
(4) The scale in the pipe is easy to remove, and there is no need to stop the refrigeration system.
(5) The temperature rise of the cooling water in the vertical condenser is generally only 2 to 4°C, and the logarithmic average temperature difference is generally around 5 to 6°C, and the water consumption is relatively large.
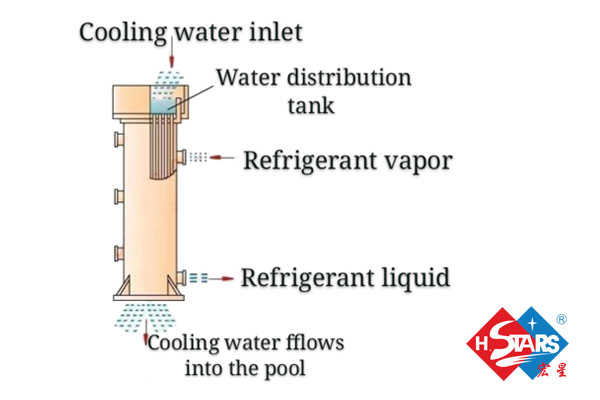
Working principle of vertical shell and tube condenser
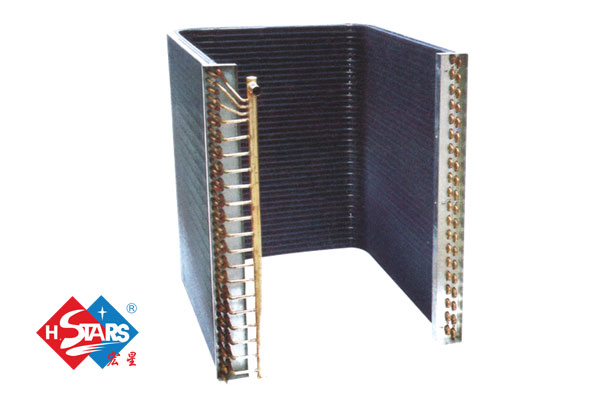
3. Features of fin type condenser
Finned condenser is the most widely used heat exchange equipment in gas and liquid heat exchangers. It achieves the purpose of enhancing heat transfer by adding fins to the ordinary base tube. The base pipe can be steel pipe, stainless steel pipe, copper pipe, etc. The fins can also use steel belt; stainless steel belt, copper belt, aluminum belt and so on. Finned heat exchangers are mainly used in air conditioning, heat pumps, and refrigeration systems.
H.Stars has been a HVACR manufacturer for more than 28 years. Customized high efficient chiller / heat pump provide -50℃ to 90℃ solution to the customer. If you are interested in our Shell and Tube Condensor, you can contact us. Email: maychow@hstars.com.cn


评论
发表评论